中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 426-431.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0042
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
CT确定胫骨前后轴指导全膝关节置换过程中胫骨假体的旋转对线
张 雷1,廉 凯2,彭 昊1,陈 森1
- 1武汉大学人民医院骨关节外科,湖北省武汉市 430060;2襄阳市中心医院骨科,湖北省襄阳市 441021
Tibial anteroposterior axis measured by CT scan in optimizing tibial prosthesis rotation during total knee arthroplasty
Zhang Lei1, Lian Kai2, Peng Hao1, Chen Sen1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Xiangyang Central Hospital, Xiangyang 441021, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
股骨外科上髁轴:是股骨外上髁最突点与内上髁最凹点的连线,股骨临床上髁轴是股骨外上髁最突点与股骨内上髁最突点的连线,而股骨外科上髁轴是目前最可靠的股骨假体旋转安放的参考线,可能因为股骨外科上髁轴与膝关节屈曲活动旋转轴非常符合,而且是股骨侧副韧带的起点,但由于骨性关节炎骨质的增生,使得这些解剖标志在术中较难确定,因此利用价值受到限制。
胫骨前后轴:即垂直股骨外科上髁轴的轴线并通过后交叉韧带的中点。该概念的提出有以下几点理由:股骨外科上髁轴近似于膝关节屈伸活动的旋转轴,且膝关节置换术的股骨假体的外旋放置常以股骨外科上髁轴为参照;其次,膝关节伸直位位时胫骨假体与股骨假体前后轴相互平行;再次,位于胫骨后侧髁间窝的后交叉韧带被认为位于膝关节的中心。
摘要
背景:传统全膝关节置换的截骨及假体安放大多根据目测来完成,缺乏较为精确化的测量。
目的:通过全膝关节置换前CT测定胫骨前后轴的方法,确定胫骨假体的旋转对线;并与传统胫骨假体安放全膝关节置换的临床疗效进行对比分析。
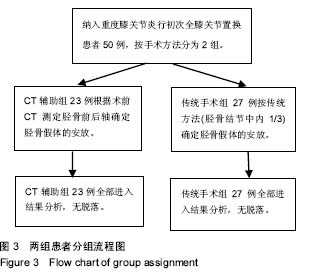
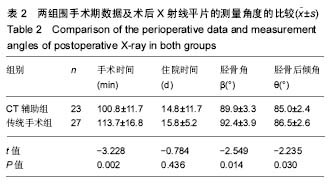
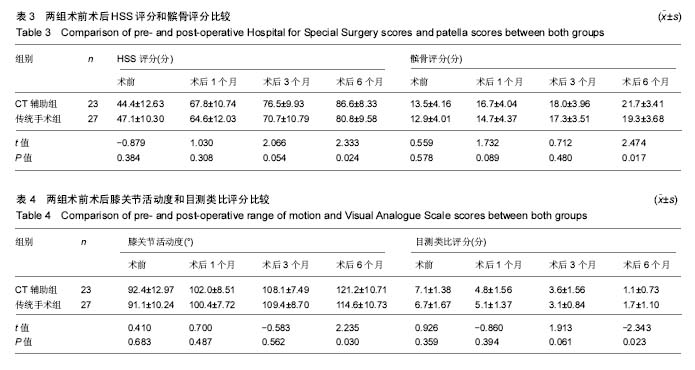
方法:回顾2014年1月至2015年4月武汉大学人民医院骨科收治的重度膝关节炎行初次全膝关节置换患者50例,根据手术方式分为2组,CT辅助组23例(25膝)经术前CT测定胫骨前后轴确定胫骨假体的安放;传统手术组 27(29膝)经传统方法(胫骨结节中内1/3)确定胫骨假体的安放。记录2组患者的手术时间及住院时间;术前和术后评估美国特种外科医院评分、髌骨评分、膝关节活动度及目测类比评分;术后3 d拍摄X射线平片测量胫骨角β和胫骨后倾角θ。所有手术均有同一团队完成。
结果与结论:①所有患者均得到随访,2组患者一般情况比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②CT辅助组的手术时间、胫骨角β及胫骨后倾角θ方面均小于传统手术组(P < 0.05),但2组在住院时间上差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③2组术前及术后1,3个月美国特种外科医院评分、髌骨评分、膝关节活动度及目测类比评分比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);术后6个月2组患者上述指标比较,CT辅助组均优于传统手术组(P < 0.05);④结果提示,术前CT测定胫骨前后轴指导胫骨假体安放较传统方法更精确定位,使股骨假体与胫骨假体有更好的旋转对线。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9872-5215(张雷)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)